BREAKING THE SOFTMAX BOTTLENECK: A HIGH-RANK RNN LANGUAGE MODEL
ICLR2018
Abstract
将LM看做是一个matrix分解的问题,现有的softmax-based models会受限于Softmax bottleneck。作者证明了,使用对于分布式的word embedding 使用softmax没有能力model language。
作者提出了MoS的方法,改进了softmax。
Introduction
LM的问题可以归结为通过某个word的上下文context,预测next-token.
这是一个conditional probability问题。
通常的方法,使用rnn将context编码成一个vector,然后通过softmax求得条件概率,这种方法会很大程度的改变了context。
基于softmax的方法是没有足够能力去model language的。这就是softmax bottleneck。
作者提出Mixture of Softmaxes
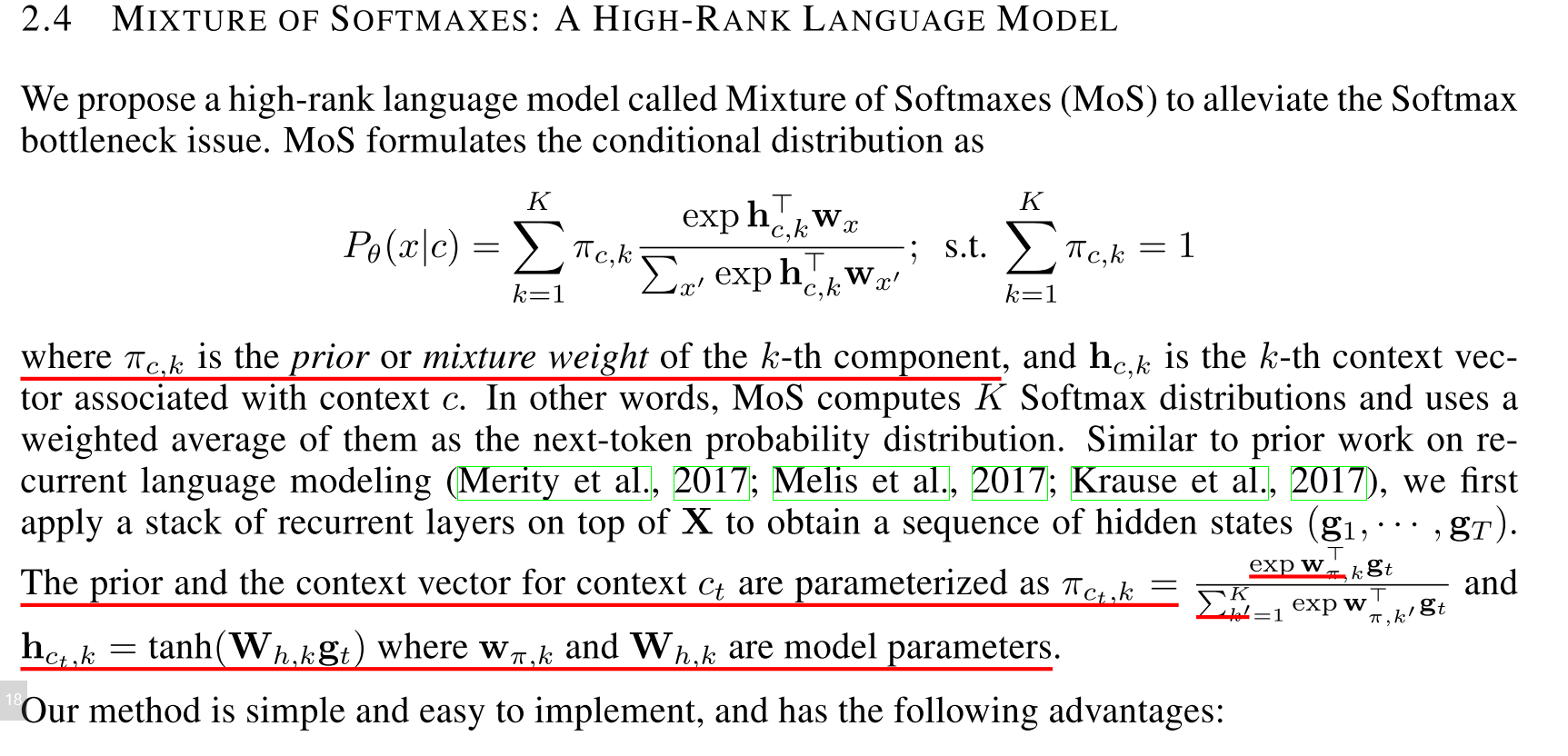
作者的github有开源MoS的代码,但是是pytorch版本的,项目需要使用tf,所以就自己改写了,发现,运行速度上要比NCE慢了许多,对比来看,NCE对于训练的加速还是很明显的。训练结果来看,MoS会更好点。
tf实现的代码:
1 | # coding: utf-8 |